Fluorine Number Of Electrons
- What Is The Mass Number For F
- Fluorine Number Of Electrons Gained Or Lost
- Fluorine Number Of Electrons Gained Or Lost
- Fluorine Number Of Electrons To Gain
- Fluorine Number Of Electrons To Lose
Fluorine has 7 valence electrons. What type of bond is likely to form between two atoms of fluorine? A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. If a fluorine atom gains an electron, it becomes a fluoride ion with an electric charge of -1. Click to see full answer. Subsequently, one may also ask, does fluorine gain or lose electrons?
Click to see full answer.
Also asked, does fluorine gain or lose electrons?
It can lose one of its electrons, making it an ion. It now has more positive protons than electrons so it has an overall positive charge. A fluorine atom will tend to gain, rather than lose, an electron. By gaining a negative electron, it has an overall negative charge.
Furthermore, what happens when an atom gains an electron? However, if something happens to make an atom lose or gain an electron then the atom will no longer be neutral. An atom that gains or loses an electron becomes an ion. If it gains a negative electron, it becomes a negative ion. If it loses an electron it becomes a positive ion (see page 10 for more on ions).
Also Know, how many electrons does fluorine gain or lose?

Example 1: A fluorine atom can get a full valence shell by either gaining one more electron, or by losing seven electrons. The former requires the transfer of less electrons, so the fluorine atom will try to gain one electron first. Therefore, F− ions are more common than F7+ ions.
What happens when fluorine atoms react?
Fluorine is in Group 7. It has seven electrons in its outer shell. It gains an electron from another atom in reactions, forming a fluoride ion, F-. A fluoride ion has the same electronic structure as a neon atom (Ne).
Element Fluorine - F
Comprehensive data on the chemical element Fluorine is provided on this page; including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides of Fluorine. Common chemical compounds are also provided for many elements. In addition technical terms are linked to their definitions and the menu contains links to related articles that are a great aid in one's studies.
Fluorine Menu
- Fluorine Page One
- Fluorine Page Two
- Fluorine Page Three
Overview of Fluorine
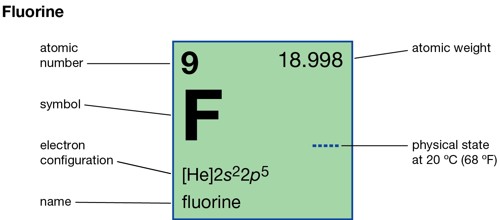
- Atomic Number: 9
- Group: 17
- Period: 2
- Series: Halogens
Fluorine's Name in Other Languages
- Latin: Fluorum
- Czech: Fluor
- Croatian: Fluor
- French: Fluor
- German: Fluor - r
- Italian: Fluoro
- Norwegian: Fluor
- Portuguese: Flúor
- Russian: Фтор
- Spanish: Flúor
- Swedish: Fluor
Atomic Structure of Fluorine
- Atomic Radius: 0.57Å
- Atomic Volume: 17.1cm3/mol
- Covalent Radius: 0.72Å
- Cross Section (Thermal Neutron Capture)σa/barns: 0.0096
- Crystal Structure: Cubic
- Electron Configuration:
- 1s2 2s2p5
- Electrons per Energy Level: 2,7
- Shell Model
- Shell Model
- Ionic Radius: 1.33Å
- Filling Orbital: 2p5
- Number of Electrons (with no charge): 9
- Number of Neutrons (most common/stable nuclide): 10
- Number of Protons: 9
- Oxidation States: -1
- Valence Electrons: 2s2p5
- Electron Dot Model
- Electron Dot Model
Chemical Properties of Fluorine
What Is The Mass Number For F
- Electrochemical Equivalent: 0.70883g/amp-hr
- Electron Work Function:
- Electronegativity: 3.98 (Pauling); 4.1 (Allrod Rochow)
- Heat of Fusion: 0.2552kJ/mol
- Incompatibilities:
- Water, nitric acid, oxidizers, organic compounds
- Ionization Potential
- First: 17.422
- Second: 34.97
- Third: 62.707
- Valence Electron Potential (-eV): -10.1
Fluorine Number Of Electrons Gained Or Lost
Physical Properties of Fluorine
Fluorine Number Of Electrons Gained Or Lost
- Atomic Mass Average: 18.9984
- Boiling Point: 85.1K -188.05°C -306.49°F
- Coefficient of lineal thermal expansion/K-1: N/A
- Conductivity
- Electrical:
Thermal: 0.000279 W/cmK
- Electrical:
- Density: 1.696g/L @ 273K & 1atm
- Description:
- Greenish-yellow gas of the Halogen family
- Enthalpy of Atomization: 79.08 kJ/mole @ 25°C
- Enthalpy of Fusion: 0.26 kJ/mole
- Enthalpy of Vaporization: 3.31 kJ/mole
- Flammablity Class: Non-flammable gas (extreme oxidizer)
- Freezing Point:see melting point
- Heat of Vaporization: 3.2698kJ/mol
- Melting Point: 53.63K -219.52°C -363.14°F
- Molar Volume: 17.1 cm3/mole
- Optical Refractive Index: 1.000195
- Physical State (at 20°C & 1atm): Gas
- Realitive Gas Density (Air=1) = 1.31
- Specific Heat: 0.82J/gK
Fluorine Number Of Electrons To Gain
Regulatory / Health
Fluorine Number Of Electrons To Lose
- CAS Number
- 7782-41-4 cryogenic liquid
- UN/NA ID and ERG Guide Number
- 1045 / 124 compressed
- 9192 / 167 cryogenic liquid
- RTECS: LM6475000
- NFPA 704
- Health:
- Fire:
- Reactivity:
- Special Hazard: OxidizerOSHAPermissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
- 1 ppm = 1.55mg/m3 @ 25°C & 1 atm
- TWA: 0.1 ppm
- OSHA PEL Vacated 1989
- TWA: 0.1 ppm
- NIOSHRecommended Exposure Limit (REL)
- TWA: 0.1 ppm
- IDLH: 25 ppm
- Routes of Exposure: Inhalation; Skin and/or eye contact
- Target Organs: Eyes, skin, respiratory system, liver, kidneys
- Levels In Humans:
Note: this data represents naturally occuring levels of elements in the typical human, it DOES NOT represent recommended daily allowances.- Blood/mg dm-3: 0.5
- Bone/p.p.m: 2000-12,000
- Liver/p.p.m: 0.22-7
- Muscle/p.p.m: 0.05
- Daily Dietary Intake: 0.3-0.5 mg
- Total Mass In Avg. 70kg human: 2.6 g
Who / Where / When / How
- Discoverer: Henri Moissan
- Discovery Location: Paris France
- Discovery Year: 1886
- Name Origin:
- Latin: fluo (flow).
- Abundance of Fluorine:
- Earth's Crust/p.p.m.: 950
- Seawater/p.p.m.:
- Atlantic Suface: 0.0001
- Atlantic Deep: 0.000096
- Pacific Surface: 0.0001
- Pacific Deep: 0.00004
- Atmosphere/p.p.m.: N/A
- Sun (Relative to H=1E12): 0.000363
- Sources of Fluorine:
- Found in the minerals fluorite (CaF2) and cryolite (Na2AlF6). Around 2,400 tons of fluorine gas and 4,700,000 tons of fluorite are produced each year. Primary mining areas are Canada, USA, UK, Russia, Mexico and Italy.
- Uses of Fluorine:
- Combines more readily than any other element. Used in refrigerants and other chloro fluorocarbons. Also in toothpaste as sodium fluoride (NaF) and stannous fluoride (SnF2); also in Teflon.
- Additional Notes:
- Fluorine gas is highly toxic and corrosive. Even exposure to low concentrations causes lung and eye irritation. Metal fluorides are also very toxic while organic fluorides are often quite harmless.
Fluorine Menu
- Fluorine Page One
- Fluorine Page Two
- Fluorine Page Three
References
A list of reference sources used to compile the data provided on our periodic table of elements can be found on the main periodic table page.
Related Resources
- Anatomy of the Atom
Answers many questions regarding the structure of atoms. - Molarity, Molality and Normality
Introduces stoichiometry and explains the differences between molarity, molality and normality. - Molar Mass Calculations and Javascript Calculator
Molar mass calculations are explained and there is a JavaScript calculator to aid calculations. - Chemical Database
This database focuses on the most common chemical compounds used in the home and industry.
Citing this page
If you need to cite this page, you can copy this text:
Kenneth Barbalace. Periodic Table of Elements - Fluorine - F. EnvironmentalChemistry.com. 1995 - 2021. Accessed on-line: 4/24/2021
https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/F.html
.Linking to this page
If you would like to link to this page from your website, blog, etc., copy and paste this link code (in red) and modify it to suit your needs:
<a href='https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/F.html'>echo Periodic Table of Elements: Fluorine - F (EnvironmentalChemistry.com)</a>- Comprehensive information for the element Fluorine - F is provided by this page including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides and technical terms are linked to their definitions.
.NOTICE: While linking to articles is encouraged, OUR ARTICLES MAY NOT BE COPIED TO OR REPUBLISHED ON ANOTHER WEBSITE UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
PLEASE, if you like an article we published simply link to it on our website do not republish it.
